Pleural Effusion Cat Ultrasound
Five cats without radiographic pleural effusion were later confirmed to have pleural effusion via thoracic ultrasound. Found with right congestive heart failure, obstruction to lymphatic drainage by tissue adhesions in pleural space, lung lobe torsion, neoplasms and abdominal contents herniating.

Pleural Effusion In A Cat Ultrasound Fip - Youtube
Ultrasound protocols are highly sensitive and specific for the detection of pleural effusion, alveolar interstitialsyndromeandpneumothorax.

Pleural effusion cat ultrasound. The therapeutic intervention also provides your first diagnostic test. Cats with pleural effusion often have severe respiratory compromise at presentation. Cats with pleural effusion often have rapid, shallow breathing and pet owners may notice increased respiratory effort.
The transducer is perpendicular to the ribs. In the moving clip, however, you can actually see the separation of the right ventricular free wall from the pericardium in a cat. Pleural effusion can have a number of different causes, including diseases of the heart, lungs, or other systemic diseases.
Pleural effusion is present in both hemithoraces (e). Thoracic radiographs usually reveal pleural effusion. Approximately 1 million people develop this abnormality each year in the united states.
Patients most commonly present with dyspnea, initially on exertion, predominantly dry cough, and pleuritic chest pain. Cats presenting with pleural effusion are nearly always in respiratory distress, ranging from an increased respiratory rate and effort to open mouth breathing. Histopathology and cultures revealed fungal pneumonia and pyothorax caused by aspergillus fumigatus.
Pleural effusion can have a number of different causes, including diseases of the heart, lungs, or other systemic diseases. This procedure removes excess fluid from the pleural space using a needle which not only relieves pressure on your cat’s lungs but also provides your veterinarian with pleural fluid samples. Some affected cats may also cough.
Caudal is to the left of the image. The chest wall may seem incompressible in cats with thoracic effusion. Of the cats that received thoracic ultrasound, most exhibited bilateral pleural effusion (93%).
Four standard effusion types recognized (in addition to blood): Pleural effusions may result from pleural, parenchymal, or extrapulmonary disease. The cat underwent exploratory thoracotomy and a total left pneumonectomy was performed.
The transducer is perpendicular to the ribs. In the below clip from the sonoscape s2, you can actually see the separation of the right ventricular free wall from the pericardium in a. Learning to perform a focused thoracic ultrasound scan or “tfast” is extremely useful.
Medical records were evaluated for final diagnosis. It can pose a diagnostic dilemma to the treating physician because it may be related to disorders of the lung or pleura, or to a systemic disorder. Careful handling and prompt and adequate stabilisation, incorporating supplemental oxygen.
Cats with pleural effusion often have severe respiratory compromise at the time of presentation. Pleural effusion refers to an accumulation of fluid within the pleural cavity. Additional findings in patients with pyothorax may include depression, anorexia, weight loss, dehydration, muffled heart and lung sounds, and pale mucous membranes.
World small animal veterinary association congress proceedings, 2018. How i approach a cat with pleural effusion. Professor, sydney school of veterinary science, university of sydney, camperdown, nsw, australia.
Cats with pleural effusion often have rapid, shallow breathing and pet owners may notice increased respiratory effort. His doctor (psp) has order a cat scan and upper right quadrant ultrasound for him since finding a plueral effusion on his 2nd chest xray. Thoracic ultrasound revealed a pleural effusion and a focal lung mass.
This is in accordance with the assumption that feline pleural effusion is bilateral in most cases due to communicating pleural cavities, 6,30,33 and might be a great argument for blind thoracentesis in cats with suspected effusion if confirmation by radiographs or ultrasound is not possible. (b) longitudinal ultrasound scan of the caudal thorax of a cat with pleural effusion. Pleural effusion is the accumulation of fluid in the pleural space resulting from disruption of the homeostatic forces responsible for the movement of pleural fluid.
In the latter situations, therapeutic intervention must be initiated quickly to prevent respiratory arrest. A pleural effusion is an excessive accumulation of fluid in the pleural space. Accumulation of fluid in the pleural space.
This fluid is usually located within the pleural sac which is a serous membrane covering the lungs. Abdominal ultrasound, repeat thoracic radiography, urinalysis with culture, and. What is a pleural effusion?
Effusion might be found more on one side than the. If the fast ultrasound does reveal pleural effusion, thoracentesis can be carried out. Some affected cats may also cough.
In this cat below, it is difficult at first glance to be able to state whether this effusion is pleural or pericardial. The caudal vena cava (cvc) is seen extending from the liver (l) to the heart (h). Unlike with a pericardial effusion, in the case of accumulation of fluid in the pleural space, there is no collapse of the heart walls.
The pleural sac can be thought of as a plastic wrap around the lungs that can potentially hold fluid or air (a potential space). This can be performed with the cat in sternal recumbency receiving oxygen therapy, and in cases of pleural effusion or obvious left atrial enlargement gives an immediate diagnosis for the cause of dyspnoea: • in contrast to humans, veterinary studies have shown questionable sensitivity and specificity for tfastandvet bluetodetectpleuralspaceandlungpathology.1,2
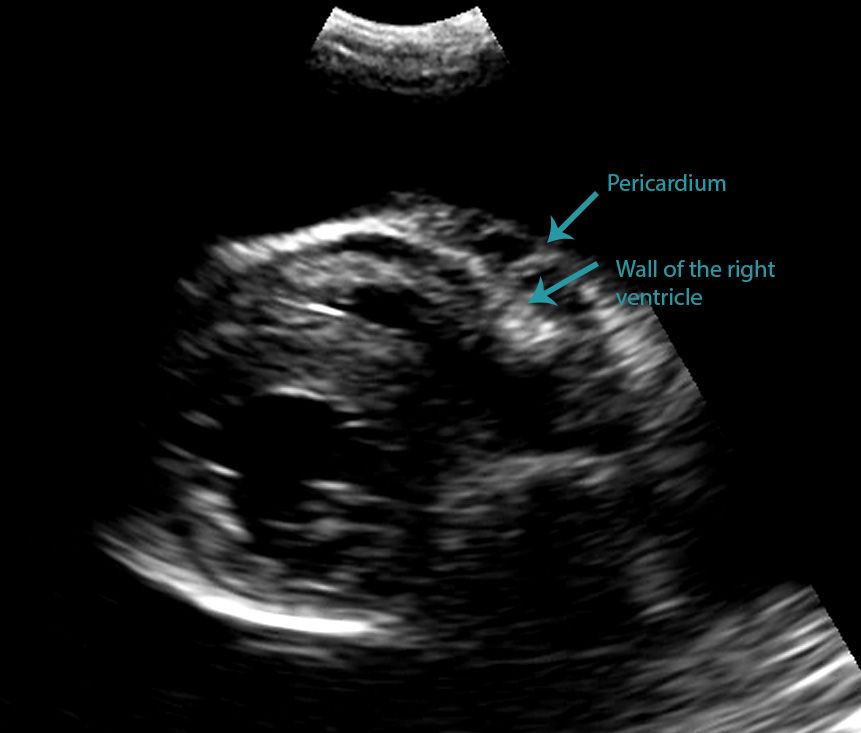
Differentiating Pericardial From Pleural Effusion - Animal Ultrasound Association

Pin By Dr Abuaiad On Lymphatics Sonography Lymph Nodes Gut Health

Pdf Thoracic Ultrasound A Method For The Work-up In Dogs And Cats With Acute Dyspnea Semantic Scholar

Pin On Fibroadenoma

Coughing Cats Are Not Cardiac Disease Vetgirl Veterinary Ce Blog Veterinary Cat Asthma Veterinary Radiology

Different Types Of Pleural Effusion On Ultrasound Scan A Exudate B Download Scientific Diagram

Differentiating Pericardial From Pleural Effusion - Animal Ultrasound Association

Large Secundum Asd With Right-sided Enlargement Sonography Student Heart Function Happy People

Fig Ure 3 Abdominal Ultrasound Images Of A 9-year-old Cat Case 4 With Download Scientific Diagram

Fig Ure 2 Abdominal Ultrasound Images Of A 6-year-old Cat Case 3 With Download Scientific Diagram

Learn How To Read A Cat X-ray Long Beach Animal Hospital Vet Medicine Radiographer X Ray

Ckd With Right Renal Cortical Cyst With Left Pleural Effusion Pleural Effusion Renal Cysts

Focused Ultrasound Of Superficialsoft Tissue Swellings Masses And Fluid Collections In Dogs And Cats - Veterinary Clinics Small Animal Practice

How To Ultrasound Detection Of Pleural Fluid Case Study - Youtube

Figure 3 From Ultrasound Of The Thorax Noncardiac Semantic Scholar

Differentiating Pericardial From Pleural Effusion - Animal Ultrasound Association

Cat Of Figure 1 Thoracic Ultrasound Revealed A Mild Hypoechoic Download Scientific Diagram

Veterinary Echocardiography Newsletter 1 Effusions - Animal Ultrasound Association
Spontaneous Cholecystopleural Fistula Leading To Biliothorax And Sepsis In A Cat